True or False? Retrieving Data From an Internet Resource to Your Computer Is Called Uploading.
Introduction
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to link several billion devices worldwide. Information technology is a network of networks that consists of millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies.

The Cyberspace Messenger by Buky Schwartz in Holon.
The Internet carries an extensive range of data resource and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents and applications of the Www (World wide web), the infrastructure to support email, and peer-to-peer networks for file sharing and telephony.
The origins of the Internet date back to research commissioned by the United States authorities in the 1960s to build robust, error-tolerant communication via calculator networks.This work, combined with efforts in the United Kingdom and France, led to the primary precursor network, the ARPANET, in the U.s.a.. The interconnection of regional academic networks in the 1980s marks the beginning of the transition to the modernistic Internet.From the early 1990s, the network experienced sustained exponential growth as generations of institutional, personal, and mobile computers were connected to it.
The funding of a new U.South. courage by the National Scientific discipline Foundation in the 1980s, besides as individual funding for other commercial backbones, led to worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies, and the merger of many networks.Though the Internet has been widely used by academia since the 1980s, the commercialization of what was by the 1990s an international network resulted in its popularization and incorporation into about every aspect of mod human life. As of 2014, 38 percentage of the earth's human population has used the services of the Internet within the past year–over 100 times more people than were using it in 1995. Internet use grew rapidly in the West from the mid-1990s to early 2000s and from the late 1990s to present in the developing earth.
Contents
- 1 History
- 2 Function
- 2.1 Linking
- 2.2 Dynamic updates of web pages
- 2.iii Www prefix
- 2.4 Scheme specifiers
- iii Web security
- four Privacy
- 5 Standards
- 6 Accessibility
- 7 Internationalization
- 8 Statistics
- ix Speed issues
- 10 Spider web caching
Most traditional communications media, including telephony and television set, are being reshaped or redefined past the Internet, giving birth to new services such equally voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and Internet Protocol television (IPTV). Newspaper, book, and other print publishing are adapting to website technology, or are reshaped into blogging and web feeds. The entertainment industry, including music, film, and gaming, was initially the fastest growing online segment. The Internet has enabled and accelerated new forms of human interactions through instant messaging, Cyberspace forums, and social networking. Online shopping has grown exponentially both for major retailers and pocket-size artisans and traders. Business-to-business and financial services on the Internet affect supply chains across entire industries.
The Cyberspace has no centralized governance in either technological implementation or policies for access and usage; each constituent network sets its own policies.Only the overreaching definitions of the two main proper name spaces in the Net, the Internet Protocol address space and the Domain Name System (DNS), are directed by a maintainer organization, the Cyberspace Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN). The technical underpinning and standardization of the core protocols is an activity of the Net Applied science Job Forcefulness (IETF), a non-profit organization of loosely affiliated international participants that anyone may associate with by contributing technical expertise.
Terminology
The Net, referring to the specific global system of interconnected IP networks, is a proper nounand may be written with an initial capital letter. In the media and mutual apply it is oftentimes not capitalized, viz. the internet. Some guides specify that the word should be capitalized when used as a noun, simply not capitalized when used equally an adjective.The Internet is too often referred to every bit the Net.
Historically the word internetted was used, uncapitalized, every bit early equally 1849 as an describing word pregnant "Interconnected; interwoven". The designers of early calculator networks used internet both as a noun and as a verb in shorthand course of internetwork or internetworking, meaning interconnecting figurer networks.
The terms Net and World Wide Web are oftentimes used interchangeably in everyday speech; it is common to speak of "going on the Net" when invoking a web browser to view web pages. Nevertheless, the Earth Wide Webor the Web is only one of a large number of Internet services. The Spider web is a collection of interconnected documents (spider web pages) and other web resource, linked by hyperlinks and URLs. Every bit some other bespeak of comparison, Hypertext Transfer Protocol, or HTTP, is the linguistic communication used on the Web for information transfer, still it is just one of many languages or protocols that can be used for communication on the Net.
The term Interweb is a portmanteau of Cyberspace and World Broad Spider web typically used sarcastically to parody a technically unsavvy user.
History

Text from the very commencement message ever sent via the ARPANET.
Inquiry into packet switching started in the early 1960s and packet switched networks such as Marker I at NPL in the United kingdom, ARPANET, CYCLADES, Merit Network, Tymnet, and Telenet, were developed in the late 1960s and early 1970s using a diversity of protocols. The ARPANET in item led to the evolution of protocols for internet working, where multiple divide networks could be joined together into a network of networks.
The starting time ii nodes of what would become the ARPANET were interconnected between Leonard Kleinrock'due south Network Measurement Center at the UCLA'due south School of Applied science and Engineering and Douglas Engelbart'southward NLS system at SRI International (SRI) in Menlo Park, California, on 29 Oct 1969. The third site on the ARPANET was the Culler-Fried Interactive Mathematics centre at the University of California at Santa Barbara, and the fourth was the University of UtahGraphics Department. In an early on sign of future growth, at that place were already fifteen sites continued to the young ARPANET by the end of 1971.These early years were documented in the 1972 motion-picture show Computer Networks: The Heralds of Resource Sharing.
Early international collaborations on the ARPANET were rare. European developers were concerned with developing the X.25networks.Notable exceptions were the Norwegian Seismic Array (NORSAR) in June 1973, followed in 1973 by Sweden with satellite links to the Tanum Earth Station and Peter T. Kirstein's research group in the Uk, initially at the Institute of Informatics, University of London and afterward at University College London.
In Dec 1974, RFC 675 – Specification of Internet Transmission Control Program, by Vinton Cerf, Yogen Dalal, and Carl Sunshine, used the terminternet as a shorthand for cyberspace working and afterwards RFCs repeat this utilise.Access to the ARPANET was expanded in 1981 when the National Science Foundation (NSF) developed the Informatics Network (CSNET). In 1982, the Cyberspace Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) was standardized and the concept of a world-broad network of fully interconnected TCP/IP networks called the Internet was introduced.

T3 NSFNET Backbone, c. 1992.
TCP/IP network access expanded again in 1986 when the National Science Foundation Network (NSFNET) provided access to supercomputer sites in the The states from research and education organizations, first at 56 kbit/due south and afterwards at 1.5 Mbit/due south and 45 Mbit/s.Commercial Internet service providers (ISPs) began to emerge in the late 1980s and early on 1990s. The ARPANET was decommissioned in 1990. The Internet was fully commercialized in the U.S. by 1995 when NSFNET was decommissioned, removing the last restrictions on the use of the Net to conduct commercial traffic.The Net started a rapid expansion to Europe and Australia in the mid to tardily 1980s and to Asia in the late 1980s and early 1990s.
Since the mid-1990s the Internet has had a tremendous impact on culture and commerce, including the ascent of near instant advice by email, instant messaging, Voice over Net Protocol (VoIP) "phone calls", two-way interactive video calls, and the World wide webwith its word forums, blogs, social networking, and online shopping sites. Increasing amounts of information are transmitted at college and higher speeds over fiber optic networks operating at 1-Gbit/s, ten-Gbit/south, or more than.
| 2005 | 2010 | 2014 a | |
| World population | 6.5 billion | half-dozen.9 billion | 7.ii billion |
| Not using the Internet | 84% | 70% | threescore% |
| Using the Cyberspace | 16% | 30% | 40% |
| Users in the developing world | 8% | 21% | 32% |
| Users in the developed world | 51% | 67% | 78% |
| aEstimate. Source: International Telecommunications Union. | |||
The Internet continues to grow, driven by ever greater amounts of online data and knowledge, commerce, entertainment and social networking. During the late 1990s, information technology was estimated that traffic on the public Internet grew by 100 percent per yr, while the hateful almanac growth in the number of Cyberspace users was thought to be between xx% and l%.This growth is frequently attributed to the lack of central administration, which allows organic growth of the network, as well every bit the not-proprietary open nature of the Internet protocols, which encourages vendor interoperability and prevents any i company from exerting also much control over the network.As of 31 March 2011, the estimated full number of Internet users was 2.095 billion (30.2% of world population).It is estimated that in 1993 the Internet carried just 1% of the information flowing through two-way telecommunication, by 2000 this figure had grown to 51%, and by 2007 more than than 97% of all telecommunicated data was carried over the Internet.
Governance

ICANN headquarters in the Playa Vista neighborhood of Los Angeles, California, United States.
The Internet is a globally distributed network comprising many voluntarily interconnected democratic networks. Information technology operates without a central governing trunk.
The technical underpinning and standardization of the core protocols (IPv4 and IPv6) is an activity of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), a non-turn a profit organization of loosely affiliated international participants that anyone may acquaintance with past contributing technical expertise.
To maintain interoperability, the principal name spaces of the Internet are administered by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN), headquartered in the neighborhood of Playa Vista in the metropolis of Los Angeles, California. ICANN is the authority that coordinates the assignment of unique identifiers for use on the Net, including domain names, Internet Protocol (IP) addresses, application port numbers in the transport protocols, and many other parameters. Globally unified proper noun spaces, in which names and numbers are uniquely assigned, are essential for maintaining the global reach of the Internet. ICANN is governed past an international board of directors drawn from beyond the Cyberspace technical, concern, academic, and other non-commercial communities. ICANN's office in analogous the assignment of unique identifiers distinguishes it as perhaps the only central coordinating body for the global Internet.
Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) classify IP addresses:
- African Network Information Center (AfriNIC) for Africa
- American Registry for Cyberspace Numbers (ARIN) for North America
- Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC) for Asia and the Pacific region
- Latin American and Caribbean Net Addresses Registry (LACNIC) for Latin America and the Caribbean region
- Réseaux IP Européens – Network Coordination Centre (RIPE NCC) for Europe, the Middle East, and Central Asia
The National Telecommunications and Information Administration, an agency of the United States Department of Commerce, continues to have final approval over changes to the DNS root zone.
The Internet Society (ISOC) was founded in 1992 with a mission to "clinch the open development, evolution and use of the Internet for the benefit of all people throughout the world".Its members include individuals (anyone may join) equally well as corporations, organizations, governments, and universities. Amidst other activities ISOC provides an administrative home for a number of less formally organized groups that are involved in developing and managing the Internet, including: the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), Internet Architecture Lath (IAB), Internet Engineering Steering Grouping (IESG), Net Research Job Forcefulness (IRTF), and Net Research Steering Group (IRSG).
On 16 November 2005, the United Nations-sponsored World Height on the Information Society, held in Tunis, established the Cyberspace Governance Forum(IGF) to talk over Internet-related issues.
Infrastructure
The communications infrastructure of the Cyberspace consists of its hardware components and a organisation of software layers that control various aspects of the architecture.
Routing and service tiers
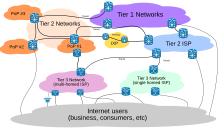
Bundle routing across the Internet involves several tiers of Internet service providers.
Internet service providers establish the globe-wide connectivity between private networks at diverse levels of scope. End-users who only admission the Internet when needed to perform a function or obtain information, represent the bottom of the routing hierarchy. At the summit of the routing bureaucracy are the tier 1 networks, large telecommunication companies that substitution traffic straight with each other via peering agreements. Tier 2 and lower level networks buyInternet transit from other providers to accomplish at least some parties on the global Internet, though they may as well engage in peering. An ISP may use a single upstream provider for connectivity, or implement multihoming to reach redundancy and load balancing. Internet exchange points are major traffic exchanges with concrete connections to multiple ISPs.
Large organizations, such as academic institutions, large enterprises, and governments, may perform the same office as ISPs, engaging in peering and purchasing transit on behalf of their internal networks. Research networks tend to interconnect with large subnetworks such as GEANT, GLORIAD, Internet2, and the Great britain'due south national research and educational activity network, JANET.
Information technology has been determined that both the Internet IP routing structure and hypertext links of the World wide web are examples of scale-complimentary networks.
Computers and routers use routing tables in their operating system to direct IP packets to the next-hop router or destination. Routing tables are maintained past transmission configuration or automatically by routing protocols. End-nodes typically use a default route that points toward an ISP providing transit, while Isp routers use the Edge Gateway Protocol to found the most efficient routing across the complex connections of the global Internet.
Admission
Common methods of Cyberspace admission by users include dial-upward with a reckoner modem via telephone circuits, broadband over coaxial cable, fiber optic or copper wires, Wi-Fi, satellite and cellular telephone technology (3G, 4G). The Internet may often be accessed from computers in libraries and Internet cafes.Internet access points exist in many public places such as drome halls and coffee shops. Various terms are used, such equally public Internet kiosk, public access terminal, and Web payphone. Many hotels also accept public terminals, though these are usually fee-based. These terminals are widely accessed for various usage, such as ticket booking, bank deposit, or online payment. Wi-Fi provides wireless access to the Internet via local computer networks. Hotspots providing such access include Wi-Fi cafes, where users need to bring their ain wireless-enabled devices such as a laptop or PDA. These services may be gratuitous to all, free to customers just, or fee-based.
Grassroots efforts have led to wireless community networks. Commercial Wi-Fi services covering big metropolis areas are in place in London, Vienna, Toronto, San Francisco, Philadelphia, Chicago and Pittsburgh. The Net tin can then exist accessed from such places every bit a park demote.Apart from Wi-Fi, there accept been experiments with proprietary mobile wireless networks like Ricochet, various high-speed information services over cellular telephone networks, and fixed wireless services. Loftier-end mobile phones such equally smartphones in general come with Cyberspace admission through the phone network. Web browsers such as Opera are available on these advanced handsets, which can as well run a wide multifariousness of other Internet software. More mobile phones have Cyberspace admission than PCs, though this is non as widely used.An Isp and protocol matrix differentiates the methods used to go online.
Protocols
While the hardware components in the Internet infrastructure can often be used to support other software systems, it is the design and the standardization process of the software that characterizes the Internet and provides the foundation for its scalability and success. The responsibility for the architectural design of the Cyberspace software systems has been assumed by the Internet Engineering Chore Force (IETF). The IETF conducts standard-setting piece of work groups, open to whatsoever private, virtually the diverse aspects of Cyberspace architecture. Resulting contributions and standards are published as Asking for Comments (RFC) documents on the IETF spider web site.
The primary methods of networking that enable the Net are independent in specially designated RFCs that constitute the Internet Standards. Other less rigorous documents are simply informative, experimental, or historical, or document the best current practices (BCP) when implementing Net technologies.
The Net standards describe a framework known every bit the Internet protocol suite. This is a model compages that divides methods into a layered arrangement of protocols, originally documented in RFC 1122 and RFC 1123. The layers represent to the environment or scope in which their services operate. At the top is the application layer, the space for the awarding-specific networking methods used in software applications. For example, a spider web browser plan uses the client-server application model and a specific protocol of interaction between servers and clients, while many file-sharing systems use a peer-to-peer image. Below this superlative layer, the transport layer connects applications on dissimilar hosts with a logical channel through the network with appropriate data exchange methods.
Underlying these layers are the networking technologies that interconnect networks at their borders and hosts via the concrete connections. The internet layeren ables computers to identify and locate each other via Internet Protocol (IP) addresses, and routes their traffic via intermediate (transit) networks. Last, at the bottom of the architecture is the link layer, which provides connectivity betwixt hosts on the same network link, such as a physical connection in class of a local area network (LAN) or a dial-upward connexion. The model, also known as TCP/IP, is designed to exist independent of the underlying hardware, which the model therefore does not concern itself with in whatever particular. Other models have been developed, such as the OSI model, that endeavour to exist comprehensive in every aspect of communications. While many similarities exist between the models, they are not compatible in the details of description or implementation; indeed, TCP/IP protocols are normally included in the discussion of OSI networking.
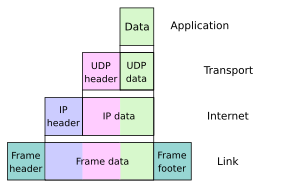
As user data is candy through the protocol stack, each brainchild layer adds encapsulation information at the sending host. Data is transmitted over the wire at the link level between hosts and routers. Encapsulation is removed by the receiving host. Intermediate relays update link encapsulation at each hop, and inspect the IP layer for routing purposes.
The well-nigh prominent component of the Internet model is the Internet Protocol (IP), which provides addressing systems (IP addresses) for computers on the Internet. IP enables internet working and in essence establishes the Internet itself. Net Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) is the initial version used on the first generation of the Cyberspace and is still in dominant utilise. Information technology was designed to address up to ~four.iii billion (109) Internet hosts. However, the explosive growth of the Net has led to IPv4 address exhaustion, which entered its concluding stage in 2011, when the global address allocation puddle was exhausted. A new protocol version, IPv6, was developed in the mid-1990s, which provides vastly larger addressing capabilities and more efficient routing of Internet traffic. IPv6 is currently in growing deployment around the world, since Internet address registries (RIRs) began to urge all resource managers to programme rapid adoption and conversion.
IPv6 is non straight interoperable past blueprint with IPv4. In essence, information technology establishes a parallel version of the Internet not directly accessible with IPv4 software. This means software upgrades or translator facilities are necessary for networking devices that need to communicate on both networks. Substantially all modern computer operating systems support both versions of the Net Protocol. Network infrastructure, however, is still lagging in this development. Bated from the complex assortment of physical connections that make up its infrastructure, the Net is facilitated by bi- or multi-lateral commercial contracts, e.yard., peering agreements, and by technical specifications or protocols that describe how to exchange data over the network. Indeed, the Internet is defined past its interconnections and routing policies.
Services
The Internet carries many network services, nearly prominently the World Broad Web, electronic mail, Internet telephony, and File sharing services.
Www

This NeXT Computer was used by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN and became the earth's first Web server.
Many people utilize the terms Internet and World wide web, or just the Web, interchangeably, but the two terms are not synonymous. The Www is only one of hundreds of services used on the Cyberspace. The Web is a global fix of documents, images and other resources, logically interrelated by hyperlinks and referenced with Compatible Resource Identifiers (URIs). URIs symbolically identify services, servers, and other databases, and the documents and resources that they tin provide. Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the main access protocol of the Www. Web services also use HTTP to let software systems to communicate in order to share and commutation business concern logic and data.
Www browser software, such as Microsoft'southward Cyberspace Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Opera, Apple'southward Safari, and Google Chrome, lets users navigate from one web page to another via hyperlinks embedded in the documents. These documents may also contain any combination of computer information, including graphics, sounds, text, video, multimedia and interactive content that runs while the user is interacting with the page. Client-side software tin can include animations, games, office applications and scientific demonstrations. Through keyword-driven Internet inquiry using search engines similar Yahoo! and Google, users worldwide have easy, instant access to a vast and diverse amount of online information. Compared to printed media, books, encyclopedias and traditional libraries, the World wide web has enabled the decentralization of information on a large scale.
The Spider web has also enabled individuals and organizations to publish ideas and data to a potentially big audience online at greatly reduced expense and fourth dimension delay. Publishing a web page, a weblog, or building a website involves lilliputian initial cost and many cost-free services are available. Even so, publishing and maintaining large, professional web sites with attractive, diverse and up-to-date data is even so a difficult and expensive proposition. Many individuals and some companies and groups utilise web logs or blogs, which are largely used as easily updatable online diaries. Some commercial organizations encouragestaff to communicate advice in their areas of specialization in the promise that visitors volition be impressed by the expert knowledge and complimentary information, and be attracted to the corporation as a effect.
One example of this practice is Microsoft, whose product developers publish their personal blogs in lodge to pique the public'southward interest in their work. Collections of personal web pages published by large service providers remain pop, and take become increasingly sophisticated. Whereas operations such every bit Angelfire and GeoCities have existed since the early days of the Web, newer offerings from, for case, Facebook and Twitter currently have large followings. These operations often brand themselves as social network services rather than only as spider web page hosts.
Advertising on pop web pages can be lucrative, and east-commerce or the sale of products and services directly via the Web continues to grow.
When the Web developed in the 1990s, a typical web page was stored in completed grade on a web server, formatted in HTML, complete for transmission to a web browser in response to a request. Over time, the process of creating and serving web pages has become dynamic, creating flexible blueprint, layout, and content. Websites are oftentimes created using content management software with, initially, very little content. Contributors to these systems, who may be paid staff, members of an organization or the public, fill underlying databases with content using editing pages designed for that purpose, while casual visitors view and read this content in HTML form. There may or may not be editorial, approval and security systems congenital into the process of taking newly entered content and making it available to the target visitors.
Communication
E-mail is an important communications service available on the Internet. The concept of sending electronic text messages between parties in a fashion analogous to mailing messages or memos predates the cosmos of the Internet. Pictures, documents and other files are sent equally electronic mail attachments. Emails can be cc-ed to multiple email addresses.
Cyberspace telephony is another common communications service made possible past the creation of the Internet. VoIP stands for Phonation-over-Internet Protocol, referring to the protocol that underlies all Internet communication. The idea began in the early 1990s with walkie-talkie-like voice applications for personal computers. In recent years many VoIP systems have become as easy to use and as user-friendly as a normal telephone. The benefit is that, every bit the Internet carries the voice traffic, VoIP can be free or cost much less than a traditional telephone telephone call, particularly over long distances and especially for those with always-on Internet connections such as cable or ADSL. VoIP is maturing into a competitive alternative to traditional phone service. Interoperability between different providers has improved and the ability to call or receive a telephone call from a traditional telephone is available. Uncomplicated, inexpensive VoIP network adapters are available that eliminate the need for a personal computer.
Phonation quality can even so vary from call to telephone call, simply is often equal to and can even exceed that of traditional calls. Remaining problems for VoIP include emergency phone number dialing and reliability. Currently, a few VoIP providers provide an emergency service, but information technology is not universally available. Older traditional phones with no "actress features" may be line-powered only and operate during a ability failure; VoIP can never do so without a backup power source for the telephone equipment and the Net access devices. VoIP has besides go increasingly popular for gaming applications, every bit a form of communication between players. Pop VoIP clients for gaming include Ventrilo and Teamspeak. Mod video game consoles also offer VoIP chat features.
Information transfer
File sharing is an example of transferring large amounts of data across the Net. A figurer file tin be emailed to customers, colleagues and friends as an attachment. It can be uploaded to a website or FTP server for easy download by others. Information technology can be put into a "shared location" or onto a file server for instant use by colleagues. The load of bulk downloads to many users tin be eased past the use of "mirror" servers or peer-to-peer networks. In any of these cases, admission to the file may exist controlled by user authentication, the transit of the file over the Net may be obscured by encryption, and coin may change hands for access to the file. The price can exist paid by the remote charging of funds from, for example, a credit menu whose details are also passed – commonly fully encrypted – beyond the Internet. The origin and actuality of the file received may be checked by digital signatures or by MD5 or other bulletin digests. These simple features of the Internet, over a worldwide basis, are changing the product, sale, and distribution of anything that can be reduced to a calculator file for transmission. This includes all manner of impress publications, software products, news, music, moving picture, video, photography, graphics and the other arts. This in turn has acquired seismic shifts in each of the existing industries that previously controlled the production and distribution of these products.
Streaming media is the existent-fourth dimension delivery of digital media for the firsthand consumption or enjoyment past finish users. Many radio and telly broadcasters provide Net feeds of their alive audio and video productions. They may too allow fourth dimension-shift viewing or listening such every bit Preview, Classic Clips and Listen Again features. These providers have been joined by a range of pure Cyberspace "broadcasters" who never had on-air licenses. This ways that an Net-connected device, such every bit a computer or something more specific, can be used to access on-line media in much the same mode every bit was previously possible only with a television or radio receiver. The range of available types of content is much wider, from specialized technical webcasts to on-demand popular multimedia services. Podcasting is a variation on this theme, where – usually audio – textile is downloaded and played back on a computer or shifted to a portable media actor to be listened to on the movement. These techniques using simple equipment allow everyone, with little censorship or licensing control, to broadcast audio-visual material worldwide.
Digital media streaming increases the demand for network bandwidth. For instance, standard epitome quality needs one Mbit/s link speed for SD 480p, Hard disk drive 720p quality requires 2.5 Mbit/south, and the top-of-the-line HDX quality needs 4.5 Mbit/s for 1080p.
Webcams are a depression-toll extension of this phenomenon. While some webcams can give full-frame-charge per unit video, the motion-picture show either is usually small or updates slowly. Internet users can watch animals around an African waterhole, ships in the Panama Canal, traffic at a local roundabout or monitor their own premises, live and in real time. Video chat rooms and video conferencing are besides popular with many uses beingness found for personal webcams, with and without two-way audio. YouTube was founded on 15 February 2005 and is at present the leading website for free streaming video with a vast number of users. Information technology uses a flash-based web thespian to stream and evidence video files. Registered users may upload an unlimited amount of video and build their own personal profile. YouTube claims that its users watch hundreds of millions, and upload hundreds of thousands of videos daily. Currently, YouTube too uses an HTML5 player.
The Internet has enabled new forms of social interaction, activities, and social associations.
Users

Internet users per 100 inhabitants

Internet users by linguistic communication.

Website content languages.
Overall Net usage has seen tremendous growth. From 2000 to 2009, the number of Net users globally rose from 394 million to one.858 billion. By 2010, 22 percent of the world'due south population had access to computers with ane billion Google searches every day, 300 million Internet users reading blogs, and 2 billion videos viewed daily on YouTube. In 2014 the globe'southward Cyberspace users surpassed 3 billion or 43.6 percent of world population, merely two-thirds of the users came from richest countries, with 78.0 per centum of Europe countries population using the Internet, followed by 57.4 percent of the Americas.
The prevalent linguistic communication for communication on the Cyberspace has been English. This may be a upshot of the origin of the Internet, every bit well equally the language'south role as a lingua franca. Early calculator systems were limited to the characters in the American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII), a subset of the Latin alphabet.
After English language (27%), the most requested languages on the World Wide Web are Chinese (25%), Spanish (viii%), Japanese (5%), Portuguese and German (iv% each), Arabic, French and Russian (3% each), and Korean (2%).By region, 42% of the world'south Internet users are based in Asia, 24% in Europe, 14% in Northward America, 10% in Latin America and the Caribbean area taken together, half-dozen% in Africa, three% in the Middle Eastward and 1% in Australia/Oceania.The Cyberspace'southward technologies take developed plenty in recent years, especially in the use of Unicode, that good facilities are available for development and communication in the world'due south widely used languages. However, some glitches such as mojibake (incorrect brandish of some languages' characters) however remain.
In an American study in 2005, the percent of men using the Internet was very slightly alee of the percent of women, although this divergence reversed in those under xxx. Men logged on more often, spent more time online, and were more likely to be broadband users, whereas women tended to make more than use of opportunities to communicate (such as email). Men were more than likely to utilize the Cyberspace to pay bills, participate in auctions, and for recreation such every bit downloading music and videos. Men and women were as likely to use the Net for shopping and banking.More recent studies indicate that in 2008, women significantly outnumbered men on nearly social networking sites, such as Facebook and Myspace, although the ratios varied with age.In improver, women watched more streaming content, whereas men downloaded more. In terms of blogs, men were more likely to blog in the first identify; among those who blog, men were more probable to have a professional weblog, whereas women were more likely to accept a personal weblog.
According to forecasts by Euromonitor International, 44% of the world'south population volition exist users of the Internet past 2020. Splitting by land, in 2012 Iceland, Norway, Sweden, holland, and Denmark had the highest Internet penetration past the number of users, with 93% or more of the population with access.
Several neologisms be that refer to Cyberspace users: Netizen (as in as in "citizen of the net")refers to those actively involved in improving online communities, the Internet in general or surrounding political affairs and rights such as free oral communication, Internaut refers to operators or technically highly capable users of the Net,digital citizen refers to a person using the Internet in social club to engage in social club, politics, and government participation.
Usage
The Internet allows greater flexibility in working hours and location, peculiarly with the spread of unmetered high-speed connections. The Internet can be accessed almost anywhere by numerous means, including through mobile Internet devices. Mobile phones, data cards, handheld game consoles and cellular routers permit users to connect to the Internet wirelessly. Within the limitations imposed by small-scale screens and other express facilities of such pocket-sized devices, the services of the Internet, including email and the web, may be available. Service providers may restrict the services offered and mobile information charges may exist significantly college than other admission methods.
Educational material at all levels from pre-school to post-doctoral is available from websites. Examples range from CBeebies, through schoolhouse and high-school revision guides and virtual universities, to access to top-end scholarly literature through the likes of Google Scholar. For distance education, help with homework and other assignments, self-guided learning, whiling away spare time, or just looking up more detail on an interesting fact, it has never been easier for people to access educational data at any level from anywhere. The Net in full general and the World Wide Web in detail are of import enablers of both formal and informal instruction. Further, the Internet allows universities, in detail researchers from the social and behavioral sciences, to conduct research remotely via virtual laboratories, with profound changes in accomplish and generalizability of findings also as in communication between scientists and in the publication of results.
The low cost and about instantaneous sharing of ideas, knowledge, and skills has made collaborative work dramatically easier, with the help of collaborative software. Not just can a group cheaply communicate and share ideas simply the wide achieve of the Cyberspace allows such groups more easily to class. An example of this is the free software movement, which has produced, amongst other things, Linux, Mozilla Firefox, and OpenOffice.org. Net chat, whether using an IRC chat room, an instant messaging organization, or a social networking website, allows colleagues to stay in touch in a very convenient style while working at their computers during the day. Messages can exist exchanged even more quickly and conveniently than via email. These systems may permit files to be exchanged, drawings and images to exist shared, or vocalism and video contact between team members.
Content management systems allow collaborating teams to piece of work on shared sets of documents simultaneously without accidentally destroying each other's work. Business and project teams can share calendars as well as documents and other information. Such collaboration occurs in a wide diversity of areas including scientific research, software development, conference planning, political activism and creative writing. Social and political collaboration is also condign more widespread equally both Internet access and calculator literacy spread.
The Internet allows figurer users to remotely access other computers and information stores easily, wherever they may exist. They may practice this with or without computer security, i.e. authentication and encryption technologies, depending on the requirements. This is encouraging new ways of working from home, collaboration and information sharing in many industries. An accountant sitting at home can audit the books of a company based in another country, on a server situated in a tertiary country that is remotely maintained by Information technology specialists in a quaternary. These accounts could have been created by domicile-working bookkeepers, in other remote locations, based on information emailed to them from offices all over the world. Some of these things were possible earlier the widespread employ of the Internet, just the cost of individual leased lines would have fabricated many of them infeasible in practise. An office worker away from their desk, perhaps on the other side of the earth on a business organisation trip or a vacation, tin can access their emails, access their information using deject calculating, or open a remote desktop session into their office PC using a secure Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection on the Net. This can give the worker complete admission to all of their normal files and data, including email and other applications, while away from the role. Information technology has been referred to among organization administrators as the Virtual Private Nightmare, because it extends the secure perimeter of a corporate network into remote locations and its employees' homes.
Social networking and entertainment
Many people employ the World wide web to access news, weather condition and sports reports, to programme and book vacations and to pursue their personal interests. People use conversation, messaging and electronic mail to brand and stay in touch with friends worldwide, sometimes in the aforementioned way as some previously had pen pals.
Social networking websites such as Facebook, Twitter, and Myspace take created new ways to socialize and interact. Users of these sites are able to add a wide multifariousness of information to pages, to pursue common interests, and to connect with others. It is also possible to detect existing acquaintances, to allow communication amid existing groups of people. Sites similar LinkedIn foster commercial and business connections. YouTube and Flickr specialize in users' videos and photographs.
While social networking sites were initially for individuals merely, today they are widely used by businesses and other organizations to promote their brands, to market to their customers and to encourage posts to "go viral". "Black hat" social media techniques are also employed by some organizations, such as spam accounts and astroturfing.
A take chances for both individuals and organizations writing posts (especially public posts) on social networking websites, is that particularly foolish or controversial posts occasionally lead to an unexpected and perhaps large-scale backlash on social media from other internet users. This is also a risk in relation to controversial offline behavior, if it is widely fabricated known. The nature of this backlash tin can range widely from counter-arguments and public mockery, through insults and hate speech, to, in extreme cases, rape and expiry threats. The online disinhibition effect describes the tendency of many individuals to behave more stridently or offensively online than they would in person. A significant number of feminist women have been the target of various forms of harassment in response to posts they take made on social media, and Twitter in item has been criticised in the past for not doing enough to aid victims of online abuse.
For organizations, such a backlash tin can cause overall brand harm, peculiarly if reported past the media. Nevertheless, this is non always the example, as any brand impairment in the optics of people with an opposing opinion to that presented by the organization could sometimes be outweighed by strengthening the brand in the optics of others. Furthermore, if an organisation or private gives in to demands that others perceive as wrong-headed, that can and then provoke a counter-backlash.
Some websites, such as Reddit, have rules forbidding the posting of personal information of individuals (also known as doxxing), due to concerns about such postings leading to mobs of big numbers of Internet users directing harassment at the specific individuals thereby identified. In particular, the Reddit rule forbidding the posting of personal information is widely understood to imply that all identifying photos and names must be censored in Facebook screenshots posted to Reddit. Yet, the interpretation of this rule in relation to public Twitter posts is less clear, and in whatsoever instance agreeing people online take many other means they tin use to straight each other's attention to public social media posts they disagree with.
Children also face dangers online such as cyberbullying and approaches by sexual predators, who sometimes pose as children themselves. Children may also encounter material which they may find upsetting, or material which their parents consider to be non age-appropriate. Due to naivety, they may likewise post personal information near themselves online, which could put them or their families at take a chance, unless warned not to exercise so. Many parents choose to enable internet filtering, and/or supervise their children'due south online activities, in an attempt to protect their children from inappropriate material on the internet. The almost pop social networking websites, such equally Facebook and Twitter, commonly forbid users under the age of 13. Even so, these policies are typically lilliputian to circumvent by registering an business relationship with a false nativity date, and a significant number of children aged nether thirteen join such sites anyway. Social networking sites for younger children, which merits to provide better levels of protection for children, also exist.
The Net has been a major outlet for leisure action since its inception, with entertaining social experiments such every bit MUDs and MOOs beingness conducted on university servers, and sense of humor-related Usenet groups receiving much traffic. Today, many Internet forums take sections devoted to games and funny videos. Over 6 1000000 people utilize blogs or message boards as a means of communication and for the sharing of ideas. The Internet pornography and online gambling industries have taken advantage of the World wide web, and often provide a significant source of advertising revenue for other websites. Although many governments accept attempted to restrict both industries' utilise of the Cyberspace, in full general this has failed to stop their widespread popularity.

Image created for a GameSpy contest.
Another area of leisure activity on the Net is multiplayer gaming. This form of recreation creates communities, where people of all ages and origins enjoy the fast-paced world of multiplayer games. These range from MMORPG to first-person shooters, from role-playing video games to online gambling. While online gaming has been around since the 1970s, modern modes of online gaming began with subscription services such as GameSpy and MPlayer.Not-subscribers were limited to certain types of game play or certain games. Many people employ the Net to access and download music, movies and other works for their enjoyment and relaxation. Free and fee-based services be for all of these activities, using centralized servers and distributed peer-to-peer technologies. Some of these sources do more than care with respect to the original artists' copyrights than others.
Internet usage has been correlated to users' loneliness.Alone people tend to utilize the Internet as an outlet for their feelings and to share their stories with others, such every bit in the "I am lonely will anyone speak to me" thread.
Cybersectarianism is a new organizational grade which involves: "highly dispersed small groups of practitioners that may remain largely anonymous within the larger social context and operate in relative secrecy, while still linked remotely to a larger network of believers who share a prepare of practices and texts, and often a common devotion to a item leader. Overseas supporters provide funding and back up; domestic practitioners distribute tracts, participate in acts of resistance, and share information on the internal situation with outsiders. Collectively, members and practitioners of such sects construct viable virtual communities of faith, exchanging personal testimonies and engaging in commonage written report via e-mail, on-line conversation rooms and web-based bulletin boards." In particular, the British government has raised concerns about the prospect of immature British Muslims beingness indoctrinated into Islamic extremism past cloth on the Cyberspace, being persuaded to join terrorist groups such equally the so-called "Islamic State", and so potentially committing acts of terrorism on returning to Britain later fighting in Syria or Iraq.
Cyberslacking can become a bleed on corporate resources; the average UK employee spent 57 minutes a day surfing the Spider web while at work, co-ordinate to a 2003 written report by Peninsula Business organization Services. Internet addiction disorder is excessive computer use that interferes with daily life. Psychologist Nicolas Carr believe that Internet use has other effects on individuals, for instance improving skills of scan-reading and interfering with the deep thinking that leads to truthful inventiveness.
Electronic business
Electronic concern (e-concern) encompasses business processes spanning the entire value concatenation: purchasing, supply chain management, marketing, sales, customer service, and concern relationship. East-commerce seeks to add revenue streams using the Internet to build and enhance relationships with clients and partners.
According to International Data Corporation, the size of worldwide e-commerce, when global business organization-to-business concern and -consumer transactions are combined, equate to $16 trillion for 2013. A report by Oxford Economics adds those two together to gauge the full size of the digital economy at $20.four trillion, equivalent to roughly thirteen.viii% of global sales.
Drawbacks
While much has been written of the economical advantages of Cyberspace-enabled commerce, at that place is also evidence that some aspects of the Net such as maps and location-aware services may serve to reinforce economic inequality and the digital divide. Electronic commerce may be responsible for consolidation and the decline of mom-and-pop, brick and mortar businesses resulting in increases in income inequality.
Author Andrew Groovy, a long-time critic of the social transformations caused by the Internet, has recently focused on the economic effects of consolidation from Cyberspace businesses. Keen cites a 2013 Institute for Local Cocky-Reliance report saying brick-and-mortar retailers employ 47 people for every $10 million in sales, while Amazon employs only 14. Similarly, the 700-employee room rental start-up Airbnb was valued at $x billion in 2014, about half equally much as Hilton Hotels, which employs 152,000 people. And car-sharing Internet startup Uber employs 1,000 full-time employees and is valued at $18.2 billion, about the aforementioned valuation as Avis and Hertz combined, which together employ near lx,000 people.
Telecommuting
Remote work is facilitated by tools such as groupware, virtual private networks, conference calling, videoconferencing, and Voice over IP (VOIP). It can be efficient and useful for companies as information technology allows workers to communicate over long distances, saving pregnant amounts of travel fourth dimension and cost. Equally broadbandInternet connections become more commonplace, more and more workers have adequate bandwidth at dwelling to utilize these tools to link their home to their corporate intranet and internal telephone networks.
Crowdsourcing
Net provides a particularly good venue for crowdsourcing (outsourcing tasks to a distributed grouping of people) since individuals tend to be more open up in spider web-based projects where they are non being physically judged or scrutinized and thus can feel more comfortable sharing.
Crowdsourcing systems are used to attain a variety of tasks. For case, the oversupply may be invited to develop a new technology, carry out a blueprint task, refine or carry out the steps of an algorithm (encounter human-based computation), or assist capture, systematize, or analyze large amounts of data (see besides citizen science).
Wikis take besides been used in the academic community for sharing and broadcasting of information beyond institutional and international boundaries. In those settings, they have been found useful for collaboration on grant writing, strategic planning, departmental documentation, and committee piece of work.The United States Patent and Trademark Role uses a wiki to allow the public to interact on finding prior art relevant to exam of awaiting patent applications. Queens, New York has used a wiki to allow citizens to collaborate on the design and planning of a local park.
The English Wikipedia has the largest user base amongst wikis on the World wide web and ranks in the top 10 among all Web sites in terms of traffic.
Politics and political revolutions

Imprint in Bangkok during the 2014 Thai coup d'état, informing the Thai public that 'like' or 'share' activities on social media could result in imprisonment (observed June 30, 2014).
The Cyberspace has achieved new relevance equally a political tool. The presidential campaign of Howard Dean in 2004 in the United States was notable for its success in soliciting donation via the Internet. Many political groups use the Net to achieve a new method of organizing for conveying out their mission, having given rise to Internet activism, most notably proficient by rebels in the Arab Bound.
The New York Times suggested that social media websites, such as Facebook and Twitter, helped people organize the political revolutions in Egypt, past helping activists organize protests, communicate grievances, and disseminate information.
The potential of the Internet as a civic tool of communicative power was explored by Simon R. B. Berdal in his 2004 thesis:
Every bit the globally evolving Internet provides ever new access points to virtual discourse forums, it besides promotes new civic relations and associations within which communicative ability may flow and accumulate. Thus, traditionally … national-embedded peripheries get entangled into greater, international peripheries, with stronger combined powers… The Net, as a result, changes the topology of the "center-periphery" model, by stimulating conventional peripheries to interlink into "super-periphery" structures, which enclose and "besiege" several centers at once.
Berdal, therefore, extends the Habermasian notion of the Public sphere to the Internet, and underlines the inherent global and civic nature that interwoven Net technologies provide. To limit the growing civic potential of the Cyberspace, Berdal likewise notes how "self-protective measures" are put in place past those threatened by information technology:
If we consider China's attempts to filter "unsuitable material" from the Internet, near of u.s. would agree that this resembles a self-protective measure past the system against the growing civic potentials of the Internet. Even so, both types represent limitations to "peripheral capacities". Thus, the Chinese regime tries to prevent communicative power to build upward and unleash (every bit the 1989 Tiananmen Foursquare uprising suggests, the government may find it wise to install "upstream measures"). Even though limited, the Net is proving to be an empowering tool too to the Chinese periphery: Analysts believe that Internet petitions take influenced policy implementation in favor of the public's online-articulated will …
Incidents of politically motivated Net censorship take now been recorded in many countries, including western democracies.
Philanthropy
The spread of low-cost Internet access in developing countries has opened upwards new possibilities for peer-to-peer charities, which allow individuals to contribute small amounts to charitable projects for other individuals. Websites, such as DonorsChoose and GlobalGiving, allow small-scale donors to direct funds to private projects of their choice.
A popular twist on Internet-based philanthropy is the utilise of peer-to-peer lending for charitable purposes. Kiva pioneered this concept in 2005, offering the beginning web-based service to publish individual loan profiles for funding. Kiva raises funds for local intermediary microfinance organizations which postal service stories and updates on behalf of the borrowers. Lenders can contribute as little as $25 to loans of their selection, and receive their coin back as borrowers repay. Kiva falls short of beingness a pure peer-to-peer charity, in that loans are disbursed before beingness funded past lenders and borrowers do non communicate with lenders themselves.
However, the contempo spread of low cost Internet access in developing countries has fabricated genuine international person-to-person philanthropy increasingly feasible. In 2009 the U.s.a.-based nonprofit Zidisha tapped into this trend to offer the first person-to-person microfinance platform to link lenders and borrowers across international borders without intermediaries. Members can fund loans for as little as a dollar, which the borrowers so use to develop concern activities that improve their families' incomes while repaying loans to the members with interest. Borrowers access the Internet via public cybercafes, donated laptops in village schools, and fifty-fifty smart phones, then create their ain profile pages through which they share photos and information about themselves and their businesses. As they repay their loans, borrowers keep to share updates and dialogue with lenders via their contour pages. This directly web-based connection allows members themselves to accept on many of the communication and recording tasks traditionally performed by local organizations, bypassing geographic barriers and dramatically reducing the cost of microfinance services to the entrepreneurs.
Security
Many computer scientists describe the Net every bit a "prime example of a big-scale, highly engineered, nonetheless highly complex organization".The structure was found to be highly robust to random failures,yet, very vulnerable to intentional attacks.
The Net construction and its usage characteristics have been studied extensively and the possibility of developing alternative structures has been investigated.
Internet resources, hardware and software components, are the target of malicious attempts to proceeds unauthorized control to cause interruptions, or access private information. Such attempts include computer viruses which re-create with the help of humans, calculator worms which re-create themselves automatically, denial of service attacks, ransomware, botnets, and spyware that reports on the activity and typing of users. Usually these activities constitute cybercrime. Defense force theorists accept too speculated about the possibilities of cyber warfare using like methods on a large scale.
Surveillance
The vast bulk of calculator surveillance involves the monitoring of data and traffic on the Net. In the United States for example, under the Communications Help For Law Enforcement Human activity, all phone calls and broadband Internet traffic (emails, spider web traffic, instant messaging, etc.) are required to be bachelor for unimpeded real-time monitoring by Federal law enforcement agencies.
Packet capture (also sometimes referred to as "packet sniffing") is the monitoring of information traffic on a computer network. Computers communicate over the Internet by breaking upwardly messages (emails, images, videos, web pages, files, etc.) into small chunks called "packets", which are routed through a network of computers, until they achieve their destination, where they are assembled back into a complete "bulletin" once again. Packet Capture Appliance intercepts these packets as they are traveling through the network, in order to examine their contents using other programs. A parcel capture is an information gathering tool, only not an assay tool. That is information technology gathers "letters" merely it does not analyze them and figure out what they mean. Other programs are needed to perform traffic analysis and sift through intercepted information looking for important/useful data. Under the Communications Assistance For Law Enforcement Act all U.S. telecommunications providers are required to install packet sniffing engineering to permit Federal constabulary enforcement and intelligence agencies to intercept all of their customers' broadband Internet and voice over Net protocol (VoIP) traffic.
In that location is far likewise much data gathered by these packet sniffers for human being investigators to manually search through all of information technology. So automated Internet surveillance computers sift through the vast corporeality of intercepted Internet traffic, and filter out and report to human investigators those bits of information which are "interesting"—such as the employ of sure words or phrases, visiting sure types of web sites, or communicating via e-mail or conversation with a certain individual or group.Billions of dollars per year are spent, by agencies such as the Information Awareness Function, NSA, GCHQ and the FBI, to develop, purchase, implement, and operate systems which intercept and analyze all of this data, and extract simply the information which is useful to law enforcement and intelligence agencies.
Similar systems are now operated by Iranian secret police force to identify and suppress dissidents. All required hardware and software has been allegedly installed by High german Siemens AG and Finnish Nokia.
Censorship
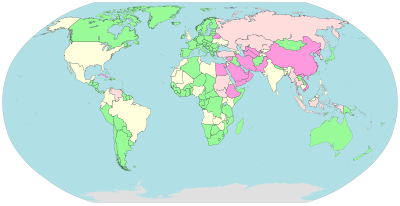
Cyberspace censorship and surveillance by country

Some governments, such every bit those of Burma, Iran, North Korea, the Mainland Communist china,Kingdom of saudi arabia and the United Arab Emirates restrict access to content on the Cyberspace within their territories, specially to political and religious content, with domain name and keyword filters.
In Norway, Denmark, Finland, and Sweden, major Internet service providers have voluntarily agreed to restrict admission to sites listed by government. While this list of forbidden resource is supposed to comprise merely known child pornography sites, the content of the list is secret. Many countries, including the United States, have enacted laws against the possession or distribution of certain material, such as child pornography, via the Internet, but exercise non mandate filter software. Many free or commercially available software programs, called content-control software are available to users to block offensive websites on private computers or networks, in order to limit access past children to pornographic material or delineation of violence.
Functioning
As the Internet is a heterogeneous network, the physical characteristics, including for example the information transfer rates of connections, vary widely. It exhibits emergent phenomena that depend on its large-calibration organization.
Outages
An Internet blackout or outage tin exist caused by local signaling interruptions. Disruptions of submarine communications cables may cause blackouts or slowdowns to big areas, such every bit in the 2008 submarine cablevision disruption. Less-developed countries are more vulnerable due to a small number of high-chapters links. Land cables are also vulnerable, as in 2011 when a woman excavation for scrap metallic severed most connectivity for the nation of Armenia.Internet blackouts affecting almost unabridged countries can be accomplished past governments as a course of Internet censorship, as in the blockage of the Internet in Egypt, whereby approximately 93% of networks were without access in 2011 in an attempt to stop mobilization for anti-regime protests.
Energy utilisation
In 2011 researchers estimated the energy used by the Cyberspace to be between 170 and 307 GW, less than two percentage of the energy used by humanity. This gauge included the free energy needed to build, operate, and periodically replace the estimated 750 million laptops, a billion smart phones and 100 one thousand thousand servers worldwide as well as the free energy that routers, cell towers, optical switches, Wi-Fi transmitters and cloud storage devices use when transmitting Internet traffic.
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/computerapps/chapter/reading-the-internet/
0 Response to "True or False? Retrieving Data From an Internet Resource to Your Computer Is Called Uploading."
Post a Comment